What is Open PGP?
Open PGP is an open source offshoot of PGP that uses PGP as its foundation. The term “Open PGP” is commonly used to describe tools, features, and solutions that support open-source PGP encryption technology.
Open PGP gives developers a way to include PGP in software that is typically free to the public. To do so, developers and vendors who include Open PGP in their software solutions must follow IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standards and allow for easy integration with other Open PGP-compliant software vendors.
Keep reading: OpenPGP, PGP, and GPG: What is the Difference?
How Open PGP Works
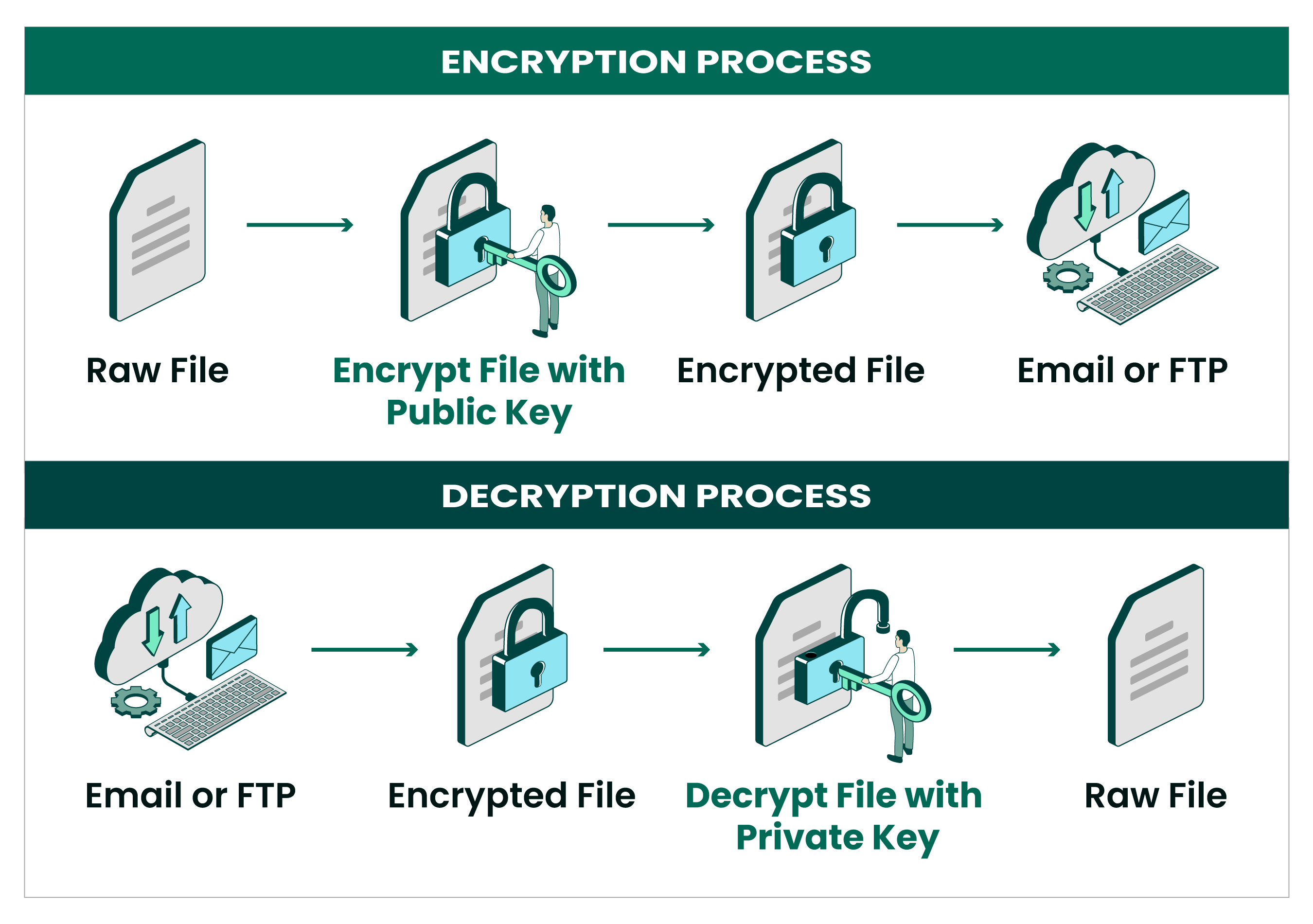
Open PGP uses asymmetric (public key) cryptography and addresses the issues of data authentication and non-repudiation through the ability to "sign" files via embedded digital signatures. According to the official OpenPGP website, even intelligence organizations aren’t able to break Open PGP encryption. These features give organizations a high level of data protection, making Open PGP one of the most popular file encryption methods used today.
Why Use Open PGP File Encryption?
Open PGP file encryption, like standard file encryption with PGP, lets you store sensitive information or transmit information across unsecure networks (i.e., the internet or email) so only the intended recipient can read it.
Open PGP’s main function is to encrypt email communication, but it can be used for a variety of use cases, which is why developers choose to incorporate Open PGP into their products.
Who Uses Open PGP?
Open PGP software is used by banks, financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and other highly regulated industries to protect their most sensitive files.
Use Open PGP for Free Today
Encrypt, decrypt, sign files, and verify documents with GoAnywhere Open PGP Studio, a free encryption solution for IT users and teams.
PGP Keys
Open PGP uses asymmetric encryption, meaning a public key is used to encrypt data and a private key is used to decrypt messages. By contrast, symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt messages:
- Anyone can use a public key.
- Private keys are known only to each user.
Encrypted data that is protected with either symmetric or asymmetric cryptography travels to the recipient who then must use PGP to decrypt the message. Data is authenticated with digital signatures using public key cryptography to ensure data is coming from the source expected and is not tampered with.
The digital signatures travel alongside the message body and use an algorithm to marry the sender’s private key with the data to be authenticated. This makes it virtually impossible to forge unless the private key is compromised.
With Open PGP, each user can use both public key cryptography as well as private. The public key encrypts files or messages and the private key decrypts the data.
How PGP Works to Send or Receive Files
- Sending files: With PGP, the sender needs access to the recipient’s public key. The session key gets encrypted with the sender’s public key and is decrypted by the recipient with their private key.
- Receiving encrypted files: The sender will need your public key. Asymmetric keys work by sharing your public PGP key with anyone who will send you encrypted information. The sender will encrypt their files using your public PGP key and you then decrypt them with your private key.
GoAnywhere MFT’s Open PGP Key Manager is an efficient way to create, export, and manage PGP keys.
Protecting PGP and PGP Keys
Administrators can set expiration dates for PGP keys to help maintain security. In addition, revocation certificates can be used to invalidate a public key, should a private key pairing be compromised
Establishing and following best practices around key management can go a long way towards protecting encrypted data and is easier with the automation features found in GoAnywhere’s key and certificate management system.
What is PGP?
PGP, Pretty Good Privacy, is a standard option for file encryption and authentication. It is currently owned by Symantec, a technology company that develops and sells software solutions.
PGP is used to encrypt files to secure them for file transfer. It uses several encryption technologies, including hashing, data compression, and public/private keys to protect sensitive information. PGP is a flexible solution for today’s cybersecurity needs: it is often used to encrypt files before exchanging them with trading partners or remote locations and can also encrypt emails, directories, and disk partitions.
How Secure is PGP?

PGP uses a combination of encryption methodologies, including hashing, data compression, symmetric-key cryptography, and public-key cryptography to secure data. It can be used to encrypt:
- Text files
- Emails
- Data files
- Directories
- Disk partitions
Ultimately, PGP is a very secure file encryption option that can be used for many purposes.
How PGP Encryption Works
By transforming plain, readable text into a complex code of unreadable characters, PGP file encryption provides essential privacy missing from online communication. Once encrypted—hashed, data compressed, and “locked” via either symmetric private key cryptography or asymmetric public key cryptography—the message travels to the recipient fully cyphered. The recipient then uses PGP to decrypt the message.
With this system, each user has both:
- An encryption key that is publicly known and can be provided to the recipient
- A private key that is known only to each user and should be kept secret
The public key encrypts the message or file, while the private key decrypts.
This encryption standard addresses the issues of data authentication and non-repudiation through the ability to "sign" files via embedded digital signatures. Digital signatures use public-key cryptography to authenticate that data is coming from the source it claims to be from and has not been tampered with. Digital signatures are sent alongside the message body and work by using an algorithm to combine the sender’s private key with the data they are authenticating. The process makes digital signatures essentially impossible to forge unless the private key has been compromised.
Keep reading: Everything You Need to Know about PGP Encryption
Sending Files with PGP
PGP is used to encrypt or decrypt the file you exchange and having a trustworthy PGP software is paramount.
For sending files with PGP, the sender will need to have access to the recipient’s public key before they can send their files. Once the file is compressed, PGP will efficiently encrypt the plaintext with private key cryptography, turning the message into ciphertext. The session key is then encrypted using the sender’s public key. Once the recipient has received the encrypted file, they can decrypt it using their private key.
The History of PGP
PGP was developed in the early 1990s by Phil Zimmermann & Associates, LLC as a method of securing files that were posted on pre-internet bulletin boards. PGP has changed ownership several times between the 90s and now, and is currently owned by Symantec.
PGP gained popularity because it was initially available freely, which made it attractive to users who wanted to encrypt files and send encrypted emails at no cost. The layers of security are also attractive and helped file encryption with PGP spread among security-conscious users – PGP uses both symmetric encryption and public key encryption, so users can send or receive messages from people they’re never met without exchanging private encryption keys.
Is PGP Still Used Today?
Although some outlets have declared that PGP is dead, PGP, Open PGP, and GPG are all still in use today, and it continues to be a secure way to encrypt your data.
What's the Difference Between PGP and GPG?
GPG, or GnuPG, is a different implementation of the Open PGP standard (more on that below), and a powerful alternative to Symantec’s official PGP software. Also known as the GNU Privacy Guard, GPG is useful in that it works well with non-GPG-based products and can open and decrypt files encrypted by PGP or Open PGP.
Keep reading: PGP vs. GPG: What’s the Difference?
PGP Solutions
There are a number of PGP solutions available and which ones organizations choose to use depends on what encryption, privacy and security requirements are needed. Here are two popular PGP solutions supported by GoAnywhere:
- Open PGP: This standard of PGP encryption is open-source for public use. The term "Open PGP" can be used to describe any program that supports the Open PGP system. Open uses asymmetric (public key) cryptography and manages data authentication and non-repudiation through the ability to "sign" files via embedded digital signatures. This provides a high level of data protection, making PGP one of the most popular encryption methods used today.
- GnuPG (GPG): GPG, also known as GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG), is an implementation of the Open PGP standard. It is an open-source option that can be used to open and decrypt files encrypted by PGP and/or Open PGP. It also provides support for S/MIME and Secure Shell (SSH). GPG is popular as it supports multiple platforms.
Prior to GoAnywhere MFT, we had to manually download our deposit files from Wells Fargo's HTTPS server on a daily basis. Now with GoAnywhere, we have scheduled those files to be downloaded automatically, which it then imports into a database on our System i server. All of the manual steps were eliminated!
Barbara Bularzik, Monterey Mushrooms, Inc.
Using MFT for PGP Decryption and Encryption
Some managed file transfer (MFT) tools, including GoAnywhere MFT, support Open PGP. Using an MFT solution gives you the ability to leverage Open PGP to:
- Encrypt files with one or more Public Keys
- Decrypt files with Private Keys
- Sign files with Private Keys
- Verify digital signatures in files using Public Keys
- Generate full audit logs of all PGP encryption and decryption processes
- Automate the entire process
Maintain the privacy and integrity of the data you exchange with external trading partners, clients, customers, and internal users when you use Open PGP via MFT.
Keep reading: 5 Benefits of PGP Decryption Using Managed File Transfer
How to Open or Decrypt a PGP File
Opening or decrypting a PGP file is easy with GoAnywhere’s Open PGP Studio. This free encryption solution lets you easily encrypt, decrypt, and sign files, as well as verify documents, to protect your sensitive files while complying with the Open PGP standard. It uses a safer, dual-key (asymmetric) system to encrypt and decrypt information.
Just download and install PGP Studio, press F1 for help and you'll get all the help you need.
To jump right to how to get started on decrypting a file in OpenPGP Studio, check out this video.
Automation of PGP in GoAnywhere MFT
- Automatically transfer files after they are encrypted with PGP
- Retrieve Open PGP files from other servers and decrypt in a workflow
- Schedule Open PGP processes to run at future dates and times
- Integrate and connect with existing applications, programs and scripts with Cloud Connectors
Open PGP Key Management
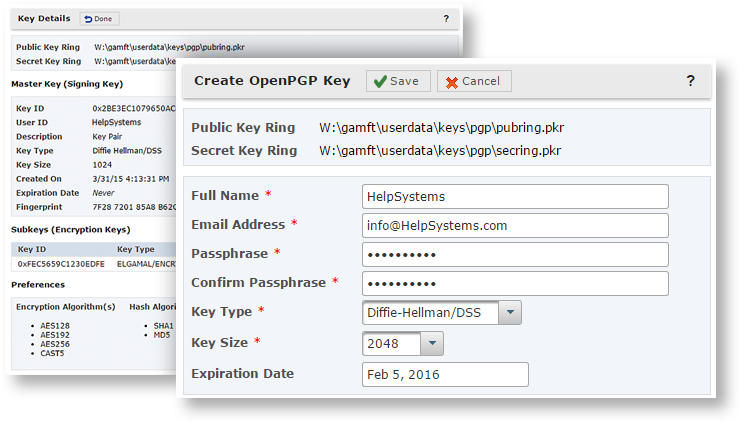
A comprehensive Open PGP Key Manager is provided in GoAnywhere MFT.
- Intuitive browser-based interface
- Create, import, export and view PGP keys
- Receive email alerts when Open PGP keys are about to expire
- Role based permissions only allow authorized users to manage PGP keys
Multi-Platform
GoAnywhere MFT can be installed to a variety of platforms to perform your Open PGP encryption and decryption processes.

Cloud Integrations
GoAnywhere connects to popular web apps that businesses and their trading partners use. Cloud Connectors integrate with a variety of technologies and help to:
- Automate your data, processes, and other tasks
- Build reusable connectors to different technologies
- Centralize your web service through GoAnywhere
Manually Encrypting a File with PGP
If not applying automation to PGP encryption you can manually encrypt a message or file by following these steps:
- First, obtain your trading partner’s public key to encrypt the file. NOTE: This is not the private key that allows your recipient to decrypt the file.
- Once you’ve received the trading partner’s public key, you can import it to a key manager or vault.
- Once that key is imported to the vault, you can create a project within your MFT software to encrypt the file to protect in transit and at rest. NOTE: Users may be required to sign the encrypted file with a private key to add an additional layer of security to the data.
This tutorial provides more extensive details.
Empower End Users to Encrypt Files Manually
If you are looking for an easy way to empower an end user, not a GoAnywhere Administrator, to encrypt files manually, another option is to use GoAnywhere’s Secure Forms module. Within Secure Forms a user can select the PGP Public Key from a drop-down list, attach the file to encrypt the file, and simply press submit to encrypt it and then get a link to download and save the PGP file. This allows the user to distribute the file as needed, or in the form itself allow the use of SFTP, Secure Mail, or other options to deliver it after encryption.
Secure Your File Movement with GoAnywhere
Start a free 30-day trial and see if GoAnywhere is the right solution for your organization.